Pitkäikäisen koripallokentän perusta
Koripallokenttä on vain niin hyvä kuin sen alla oleva alusta. Jo kauan ennen kuin laatat kiinnitetään tai kori asennetaan, pohjarakenne määrittää kentän toiminnan, käyttöiän ja sen, ilmenevätkö ongelmat kuukausien tai vuosien kuluttua.
Tämä opas keskittyy nimenomaan koripallokentän pohjarakenteen rakentamiseen. Se ei käsittele pintamateriaalin asennusta eikä korin kokoamista — nämä vaiheet tulevat myöhemmin. Oikein tehty perusta mahdollistaa kaiken muun toiminnan oikein.
Mikä on koripallokentän alusrakenne?
Alusrakenne on teknisesti suunniteltu perusta, joka tukee pelipintaa. Sen tehtävä vaikuttaa yksinkertaiselta: pysyä tasaisena, vakaana ja hallita vettä. Käytännössä tämä tarkoittaa pelaajakuormien kantamista, maan liikkeiden vastustamista ja kosteuden aiheuttamien vaurioiden estämistä yläpuolisessa kentässä.
Koripallokentillä, erityisesti modulaarista pintaa käytettäessä, alustan on oltava tasaisempi ja tarkempi kuin tavallisella terassilla, ajotiellä tai pihalaatalla. Pienet poikkeamat, jotka muualla olisivat hyväksyttäviä, voivat aiheuttaa ongelmia kentällä.
Oikean alusrakennetyypin valinta
Useimmat koripallokentät rakennetaan betonille tai asfaltille, ja betoniratkaisu on yleisimmin suosittu vaihtoehto. Se tarjoaa vakaan ja ennustettavan perustan, joka tukee tasaista pallon pomppua ja pitkäaikaista pintasuorituskykyä.
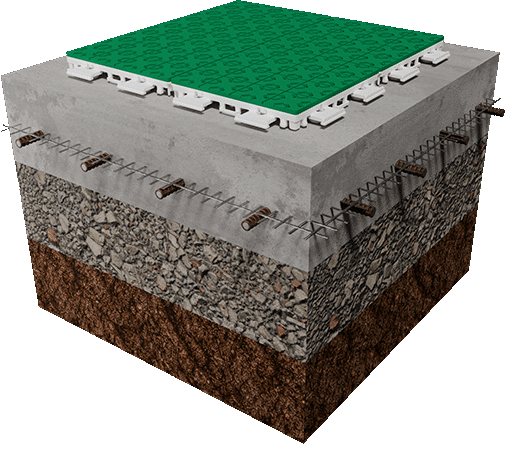
Koripallokentillä teräsbetonilaatan tulisi yleensä täyttää seuraavat kriteerit:
- Vähimmäispaksuus 100–150 mm
- Teräsverkko- tai raudoitusvahvistus
- Laserilla tasoitettu pinta
- Hienovarainen kaltevuus ulkoista vedenpoistoa varten
Asfalttialustat voivat olla sopivia tietyissä tilanteissa, mutta ne vaativat huolellisempaa valmistelua ja ovat alttiimpia pitkäaikaiselle liikkeelle.
Tasaisuuden ja toleranssien vaatimukset
Koripallokentän pinta ei anna anteeksi epätasaisia perustuksia. Toisin kuin päällysteet tai yleinen piharakentaminen, pelipinta korostaa virheitä sen sijaan, että peittäisi ne. Jopa pienet poikkeamat alusrakenteessa voivat vaikuttaa pallon pomppuun, aiheuttaa epämukavaa jalansijaa ja vaikeuttaa pinnan asennusta.
Tästä syystä koripallokentät edellyttävät korkeampaa tasaisuusvaatimusta kuin useimmat ulkobetonilaatat. Tavoitteena ei ole visuaalinen täydellisyys, vaan tasainen suorituskyky koko pelialueella. Käytännön ohjeena koripallokentän alusrakenteen tulisi täyttää seuraavat toleranssivaatimukset:
- Poikkeama enintään 3–5 mm 3 metrillä
- Ei äkillisiä korkeuseroja tai harjanteita
- Ei seisovaa vettä sateen jälkeen (ulkokentät)
Näiden toleranssien täyttäminen alusrakenteen vaiheessa ehkäisee ongelmia, joita on vaikea tai mahdoton korjata pinnan asennuksen jälkeen.
Vedenpoisto ja maapohjan valmistelu
Ulkokentillä vedenpoisto on yhtä tärkeää kuin tasaisuus. Vesi, joka ei pääse poistumaan, aiheuttaa ajan myötä liikettä, halkeamia tai routavaurioita.
Hyvä maanpohjan valmistelu sisältää yleensä tiivistetyn kivi- tai murskekerroksen laatan alla sekä hienovaraisen kallistuksen, joka ohjaa veden pois kenttäalueelta. Tavoitteena ei ole näkyvä kaltevuus, vaan seisovan veden muodostumisen estäminen pinnalle.
Vedenpoiston laiminlyönti aiheuttaa harvoin välitöntä vikaa — mutta johtaa myöhemmin hitaisiin ja kalliisiin ongelmiin.
Alusrakenteen valmiuden tarkistus
Ennen kuin jatkat koripallokentän pinnan asennusta, pysähdy ja varmista seuraavat asiat. Jos voit luottavaisin mielin rastittaa jokaisen kohdan, alusrakenne on valmis.
Alusrakenteen tulisi olla:
- Rakenteellisesti vakaa, täysin kovettunut ja halkeamaton
- Tasainen koripallokentän toleranssien mukaisesti (ei näkyviä painaumia tai harjanteita)
- Kuiva, puhdas ja roskaton
- Oikein kuivattu, ilman seisovaa vettä sateen jälkeen
- Rakennettu oikeiden mittojen ja suuntauksen mukaisesti kentän asettelua varten
Jos jokin näistä kohdista on epävarma, ratkaise se ennen pinnan asennusta. Ongelmien korjaaminen tässä vaiheessa on helppoa. Myöhemmin ei ole.
OnCourt tarjoaa tekniset piirustukset ja toleranssiohjeet urakoitsijoille, jotka rakentavat kenttien alusrakenteita.
Yleiset virheet, joita tulee välttää
Useimmat alusrakenteen ongelmat johtuvat oikoteistä eivätkä huonoista aikomuksista. Terassitasoisten toleranssien käyttö, raudoituksen pois jättäminen, valu ilman tarkkaa tasokontrollia tai kovettumisen kiirehtiminen ovat virheitä, jotka heikentävät kenttää jo ennen sen valmistumista.
- Puutteellisten toleranssien käyttö
- Ilman raudoitusta
- Valu ilman tasonhallintaa
- Asennus ennen täydellistä kovettumista
Keskeinen periaate on yksinkertainen: alusrakenteen ongelmien korjaaminen asennuksen jälkeen on huomattavasti vaikeampaa kuin sen oikea rakentaminen alusta alkaen.
Milloin alusrakenne on valmis?
Ennen pinnan asennukseen siirtymistä alusrakenteen tulee olla täysin kovettunut, puhdas ja rakenteellisesti vakaa. Sen on täytettävä tasaisuustoleranssit eikä siinä saa olla halkeamia, liikettä tai pehmeitä kohtia.
Kun nämä ehdot täyttyvät, kentän pinnan ja korin asennus on suoraviivaista.
Kenen tulisi rakentaa alusrakenne?
Vaikka monet koripallokenttien pinnat voidaan asentaa itse, alusrakenteen rakentaminen on parasta jättää kokeneille maanrakennusalan ammattilaisille. Tämä vaihe vaatii oikeat välineet, paikallisten maaperäolosuhteiden tuntemusta sekä toleranssivaatimusten ymmärtämistä, jotka ylittävät tavanomaisen piharakentamisen.
OnCourt tarjoaa tekniset piirustukset ja tekniset tiedot, jotta paikalliset urakoitsijat voivat rakentaa perustan oikein ilman arvailua. Tämä lähestymistapa yhdistää paikallisen osaamisen selkeisiin suorituskykystandardeihin.
Koripallokentän alusrakenteen UKK
Alusrakenne on kenttäpinnan alla oleva tiivistetty peruskerros. Se tukee modulilaattojärjestelmää, kantaa kuormaa, estää liikkumista ja varmistaa tasaisen pompun pallolle. Ilman kunnollista alustaa kenttä voi siirtyä, syntyä kuolleita kohtia tai vedenpoisto heikentyä ajan myötä.
Kaivusyvyys riippuu alustasta, maaperästä ja ilmastosta, mutta on tyypillisesti 100–250 mm. Pehmeässä maassa tai kylmässä ilmastossa voi olla tarpeen kaivaa syvemmälle routanousun ja painumisen estämiseksi.
Yleinen alusrakenteen kerrostus sisältää:
– Murskattua kiveä (tyyppi 1 MOT) tiivistykseen ja vedenpoistoon.
– Kerros tiivistettyä karkeaa hiekkaa tai hieno tasauskerros.
– Valinnaisesti geotekstiiliä rikkakasvien torjuntaan ja vakauteen.
Parhaan lopputuloksen saavuttamiseksi viimeistele sileällä betonilla tai asfaltilla, kun asennat modulaarisia laattoja. Kuten tässä artikkelissa mainitaan, 5 mm:n tasaisuuspoikkeama 3 m säteellä takaa hyvän suorituskyvyn.
Alustan tulee olla tasainen, sallittu poikkeama enintään 5 mm missä tahansa 3 m säteellä. Tämä tasaisuus on tärkeää, jotta modulilaatat lukittuvat kunnolla ja tarjoavat turvallisen, tasalaatuisen pelikokemuksen.
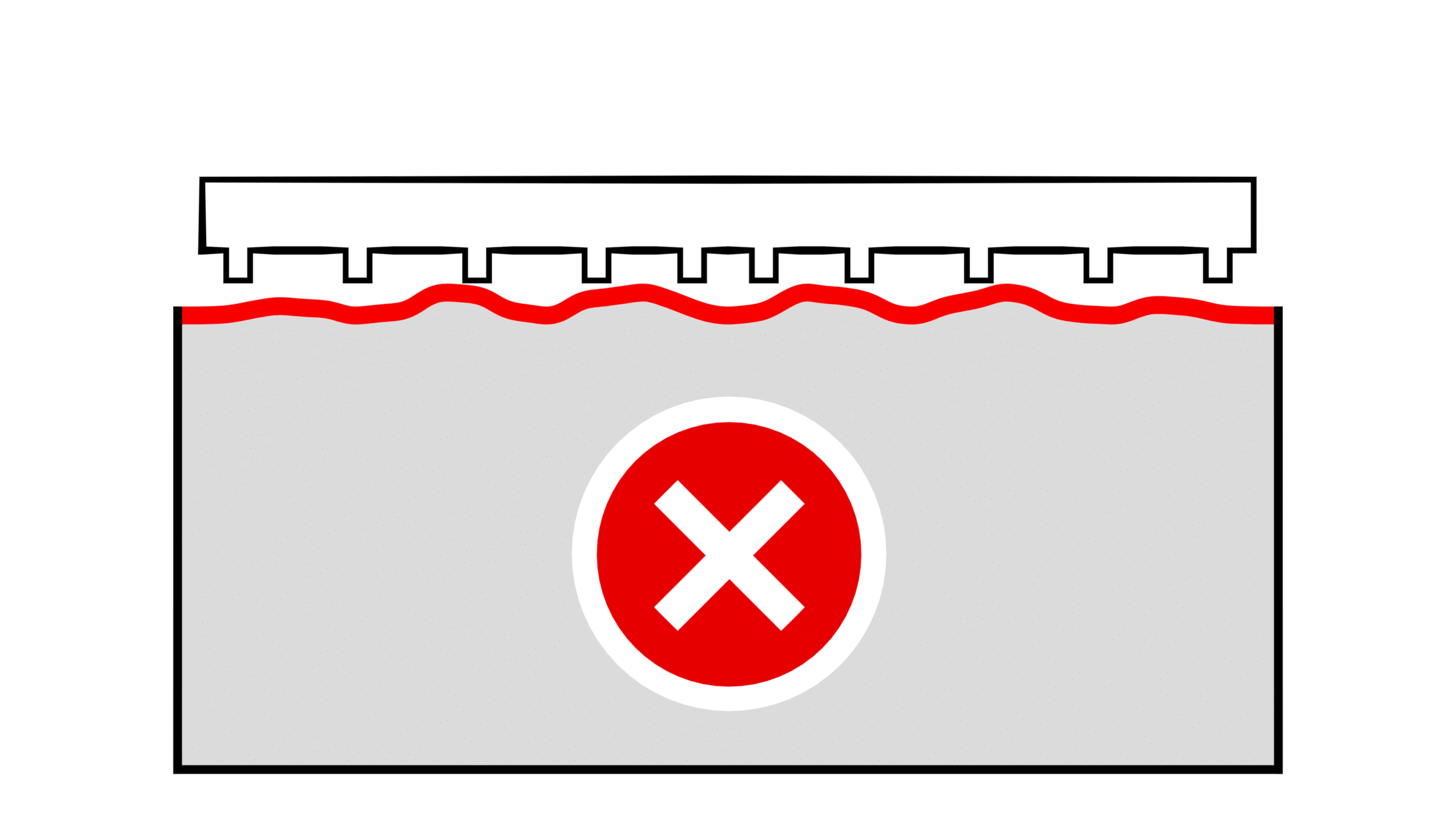
Kyllä. Oikeanlainen salaojitus estää veden kertymisen kentän modulaarisen pinnan alle. Käytä loivaa kallistusta, vettä läpäiseviä pohjakerroksia tai ojia ulkokentillä tarpeen mukaan.
Kyllä, jos sinulla on kokemusta kaivamisesta ja tiivistämisestä. Monet tekevät alustan itse, mutta suuremmissa tai monimutkaisemmissa projekteissa suosittelemme ammattilaisen palkkaamista.
Paikallinen urakoitsija on usein järkevä valinta – he tuntevat paremmin paikallisen maaperän, osaavat ratkaista alueelliset salaojaongelmat ja pystyvät järjestämään oikeat koneet ja materiaalit tehokkaasti. Ammattimaisesti tehty perusta varmistaa, että kenttäsi toimii moitteettomasti vuosien ajan.
Mega Slam -korin maahanasennus tapahtuu kahdessa vaiheessa. Ensin kaivetaan 1,25 m syvä reikä betonikiinnitystä varten. Seuraavaksi rakennetaan itse kori. Mega Slam -korit ovat raskaita – juuri siksi ne ovat paras valinta kotikäyttöön. Tarvitset muutaman avustajan nostamiseen. Mega Slam Hoopsin asennus.
HUOMAUTUS - Korin ja komponenttien ankkurit on asennettava kentän pohjarakenteen aikana. Suunnittele ja tilaa kenttä, kori ja tarvikkeet etukäteen, jotta ankkurit ovat valmiina ajoissa.
Seuraavat vaiheet
Kun alusrakenne on valmis, voit siirtyä maanrakennuksesta kentän kokoamiseen.